Casual Accounting For Derivative Instruments And Hedging Activities

Accounting for Derivatives and Hedging Activities The main issue in a ccounting for derivat ives is the treatm ent of the gains a nd losses resulting f rom the change of.
Accounting for derivative instruments and hedging activities. PowerPoint PPT presentation free to view. In this guide we attempt to clarify a complex area of accounting by providing relevant guidance and examples. Disclosures related to financial instruments both derivative and nonderivative used as hedging instruments must include A list of hedged instruments.
Its complexity stems from the underlying financial derivative instruments derivatives themselves. This Statement establishes accounting and reporting standards for derivative instruments including certain derivative instruments embedded in other contracts collectively referred to as derivatives and for hedging activities. 31 contains guidance on accounting for derivative instruments.
Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 133 FAS 133 Accounting for Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities is one of the Financial Accounting Standards Boards FASB most complex and controversial pronouncements. This comprehensive update from KPMG adds guidance on the scope of ASC 815 the definition of derivative accounting for derivatives and presentation to existing guidance on qualifying criteria and models to apply hedge accounting.
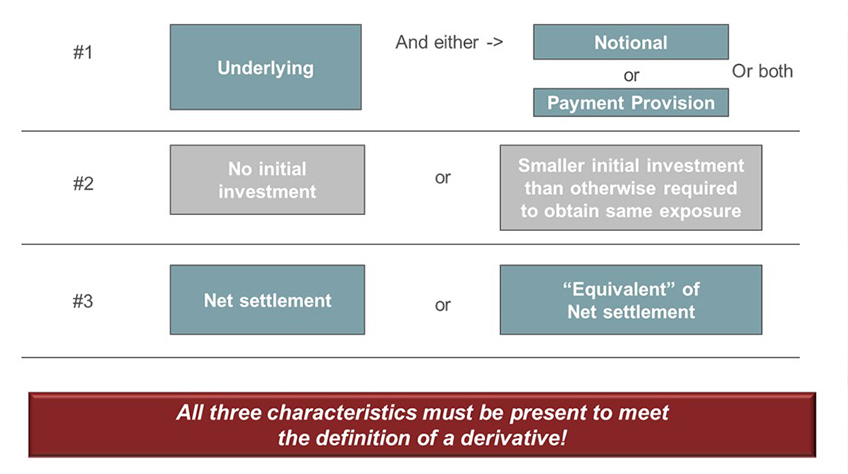
For purposes of applying the guid-ance in this section a derivative instrument is a financial instrument. Accounting for Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities Forbes School of Business Ashford University San Diego USA. The goal of this research was to investigate the reasons behind the plethora of amendments of the FASB Accounting Pronouncements for Financial Instruments from 2002 to 2008.
133 became effective for all fiscal quarters of fiscal years beginning after June 15 1999 substantiat-ing accounting and reporting standards for derivative instruments embedded derivatives and hedging activities. In developing the standards in these Provisions the following four fundamental decisions should serve as cornerstones underlying those standards. Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No.
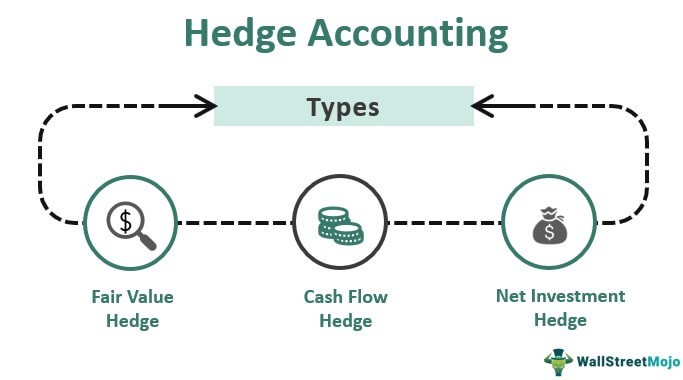
Its complexity stems from the underlying financial derivative instruments derivatives themselves. Accounting for hedges IFRS 9 broadly retains the three hedge accounting models within IAS 39 as summarised below. Under IFRS 9 hedge accounting continues to be optional and management should consider the costs and benefits when deciding whether to use it.








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/derivative.finalJPEG-5c8982d646e0fb00010f11c9.jpg)
